Introduction
In the past few years there has been an increase in the number of employees who work remotely. More and more companies are hiring remote and offshore workers because of difficulties in sourcing affordable talent close to office locations.
The purpose of this study is to understand the driving trends for remote workers and to identify some of the common challenges and difficulties faced by remote workers as they seek to build their career from a virtual location.
This study is comprised of the following elements:
- An analysis of the work/life balance of remote workers
- The extent to which remote team members can collaborate with their colleagues
- The relative productivity of remote workers to office based workers
- Benefits of hiring remote workers including cost savings
- The technology tools that are used that enable remote workers to collaborate
Although Binfire is an online project management and collaboration software company, this study does not have a technology focus and there is no reference to any particular vendor.
Summary of findings
Work/life balance issues: Remote workers are split as to whether it is more difficult to maintain a work life balance when working from home. Most remote workers do not agree that there are more distractions in home offices that reduce their productivity. In general, a majority of respondents are unconcerned that by working from home, remote workers will waste more time on non-work related websites.
Team collaboration: There is mixed response as to how well remote team members know their team members. Similarly, respondents were divided as to whether distance from team members impacts collaboration. There is more agreement that remote workers are less integrated into the corporate culture due to their long distance.
Remote worker productivity: Most respondents do not agree that working via remote makes project work more difficult. Only a minority of respondents feel that remote workers are less productive. Regarding the quality of work, 85% of respondents disagree with the notion that quality of remote work is inferior.
Cost of using remote workers: It is generally considered less expensive to hire remote workers. One of the biggest drivers is that remote workers can work longer hours without charging overtime.
Use of technology: 58% of respondents stated that collaboration is easy and also attributable to the use of collaboration tools. The most popular collaboration tool for remote teams is Skype. The second most popular tool is internal collaboration software where usage by larger organizations is more prevalent.

Work/life balance for remote workers
There is anecdotal evidence indicating that remote workers struggle with work/life balance issues. We therefore asked remote employees whether it is harder to maintain a work life balance, whether remote workers spend too much time on personal issues and the impact of personal distractions on productivity.
CHART 1: DIFFICULTY MAINTAINING WORK LIFE BALANCE
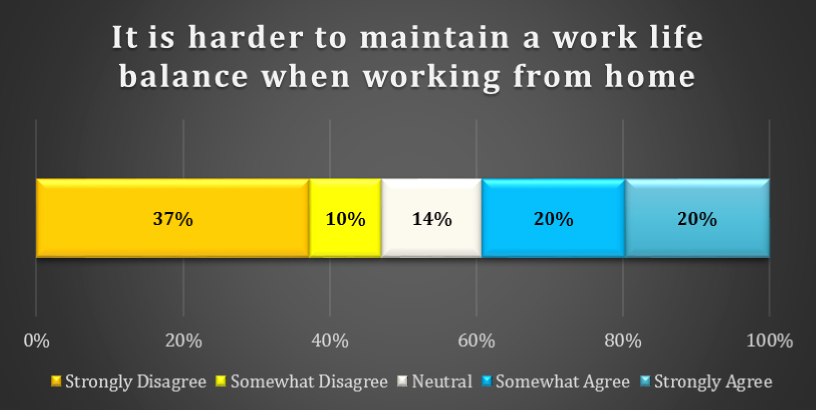
There is significant disagreement as to whether it is difficult for remote workers to maintain a work /life balance when working from home. 37% Strongly Disagree with the statement that it is harder to maintain a work life balance from home and 10% Somewhat Disagree. On the other side of the spectrum, 20% Somewhat Agree and a further 20% Strongly Agree with this statement.
chart 2: time spent on personal matters during work hours
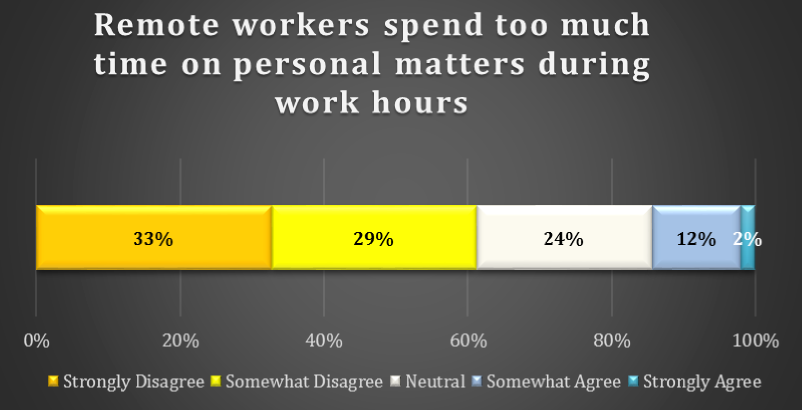
A much smaller percentage of remote workers admit to spending too much time on personal matters during the work day. Only 2% of respondents Strongly Agree that they spend too much time on personal matters. On the other side, 33% Strongly Disagree and a further 29% Somewhat Disagree that remote workers spend too much time on personal matters during work hours.
chart 3: impact of distractions on productivity
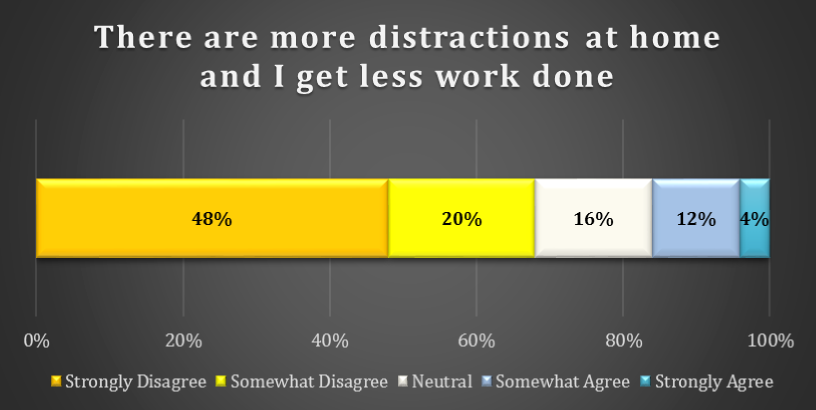
Most remote employees do not believe that working from home impairs productivity. In fact, 48% of respondents Strongly Disagree with the statement that “there are more distractions at home and I get less work done.” A further 20% Somewhat Disagree with this statement. This compares with the 4% that Strongly and the 12% that Somewhat Agree.
chart 4: impact of ONLINE distractions on productivity
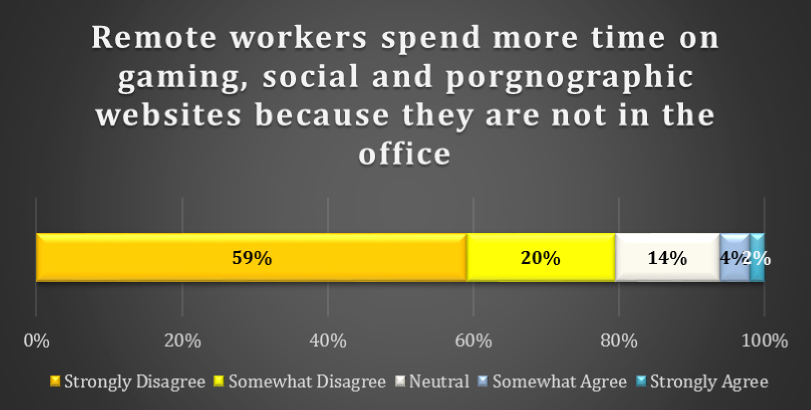
Very few respondents believe that online distractions such as gaming and social websites cause remote workers to get less work done. 59% of respondents Strongly Disagree and a further 20% Somewhat Disagree that “remote workers spend more time on gaming, social and pornographic websites because they are not in the office.”
Team Collaboration
To what extent do remote team members collaborate? How well do remote team members know their team?
chart 5: how well do remote workers know their team
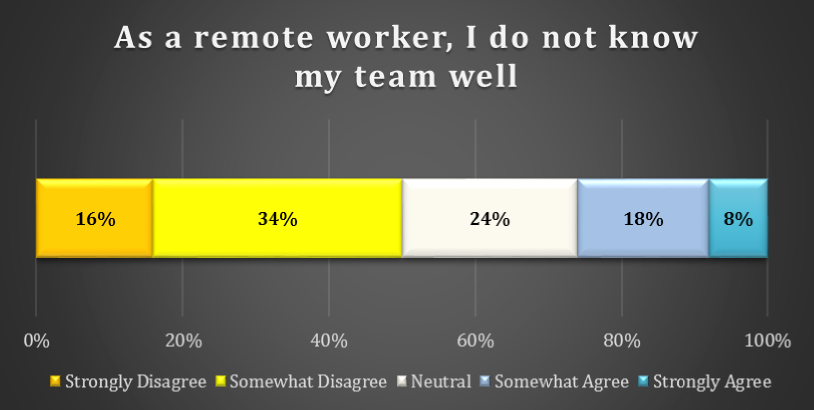
Most remote workers claim to know their team, although it is not clear from the research how well they know them. 34% of respondents Somewhat Disagree with the statement that as a “remote worker, I do not know my team well.” A further 16% Strongly Disagree with his statement. Another 24% are Neutral. Although only 8% Strongly Agree, 18% Somewhat Agree.
What conclusion can be made? Most respondents do not feel strongly about this topic and either Somewhat Agree, Somewhat Disagree or are Neutral. Perhaps remote team members do know their team members, but not as well as they would like.
chart 6: impact on colloboration due to distance from team
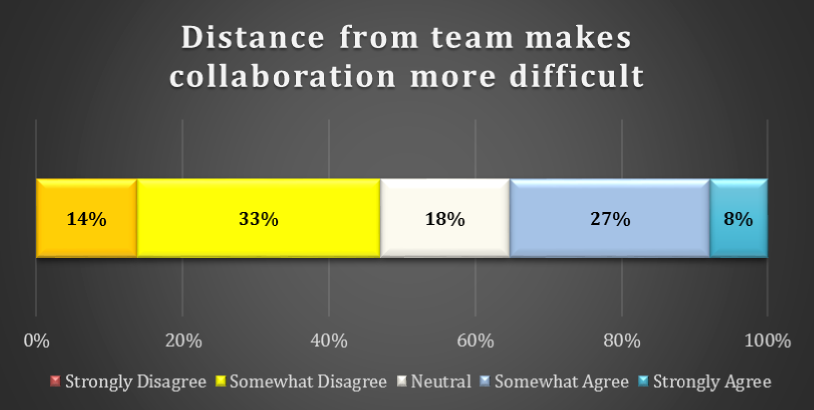
There some disagreement as to whether distance form team members make collaboration more difficult. 27% of respondents Somewhat Agree and 33% of respondents Somewhat Disagree that “distance from team members make collaboration more difficult.”
chart 7: impact on colloboration due to distance from team
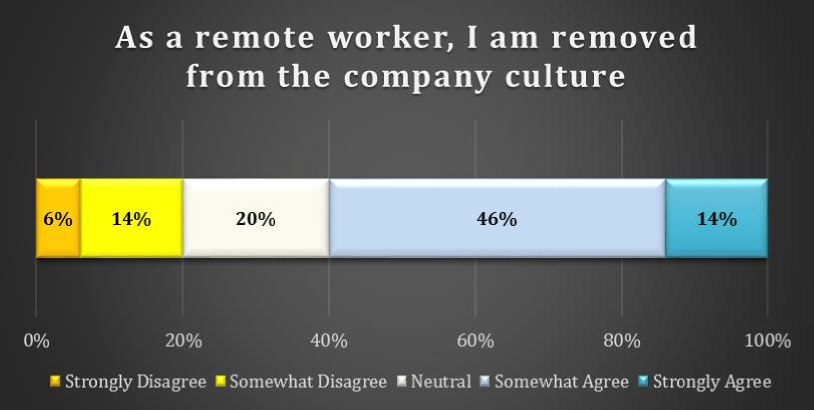
There appears to be more concern on the part of remote workers that they are removed from the corporate culture. Only 6% of respondents Strongly Disagree with the statement that as a remote worker, “I am removed from the corporate culture.” A significant number (46%) indicate that they Somewhat Agree with this statement and a further 14% Strongly Agree.
Remote Worker Productivity
To what extent does working from remote impact productivity? Are remote workers more or less productive? Our findings suggest that remote workers are just as productive as their office-base colleagues.
chart 8: Assessment of level of productivity
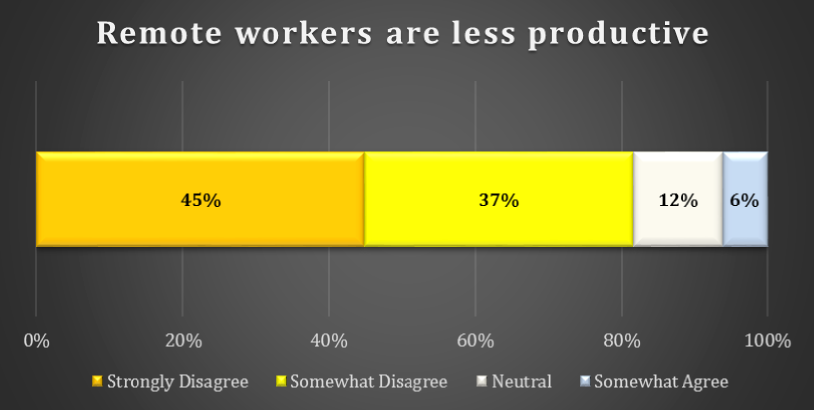
There is close to a consensus that remote workers are not less productive. A surprisingly high 45% of respondents Strongly Disagree with the notion that remote workers are less productive. A further 37% Somewhat Disagree with this. Only 6% of respondents Somewhat Agree with this statement and no one responded that they Strongly Agree.
chart 9: Assessment of quality of work
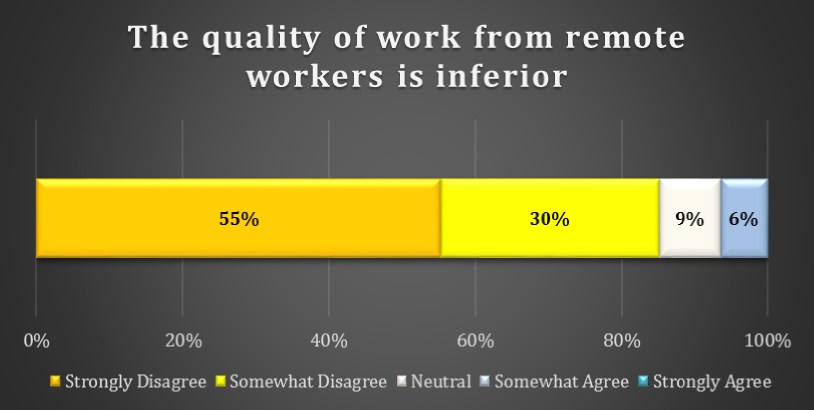
Is the quality of remote employees work inferior? According to our survey, the answer is overwhelmingly “no.” 55% of respondents Strongly Disagree that the quality of work is inferior and 30% Somewhat Disagree.
chart 10: DO REMOTE WORKERS BRING NEW PERSPECTIVES
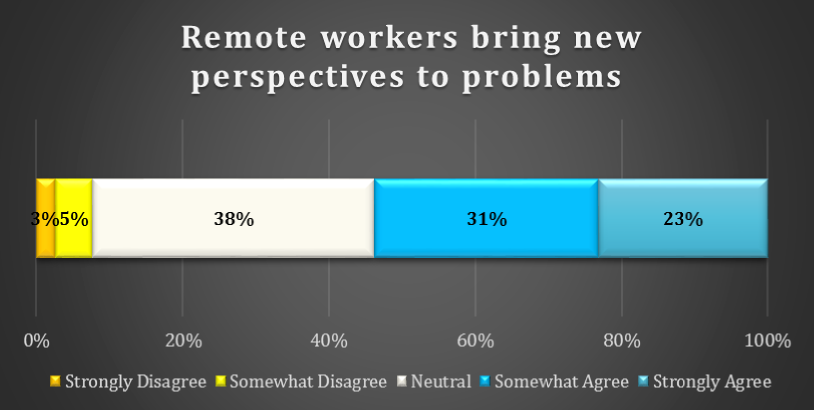
Remote workers bring new perspective to solve problems. 23% of respondents Strongly Agree with this statement and a further 31% Somewhat Agree. Interestingly, the single biggest response category was Neutral. A small minority of respondents (8%) Strongly or Somewhat Disagree.
chart 11: does remote work make projects more difficult?
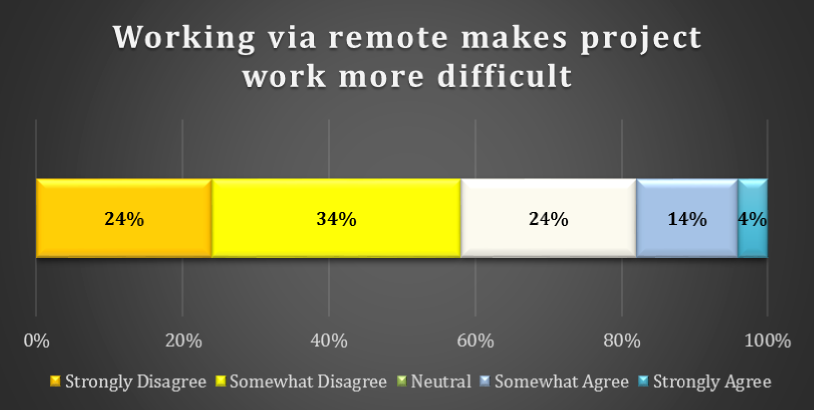
A majority of respondents do not agree that working via remote makes project work more difficult. Only 4% Strongly Agree that working via remote makes project work more difficult. 24% are Neutral. 34% of respondents Somewhat Disagree and a further 24% Strongly Disagree with the notion that working via remote makes project work more difficult.
Career Growth for Remote Workers
It has been established that remote workers are just as productive and effective as office-based workers. However, is there a sacrifice that remote employees need to make with respect to career growth?
chart 12: career growth within the organization
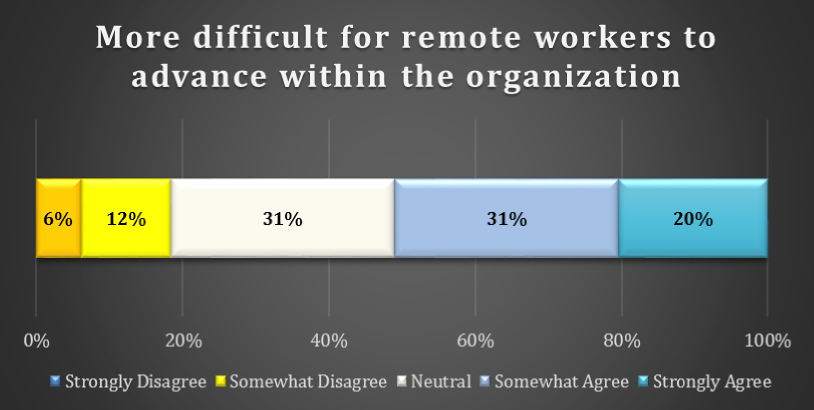
Less than 20% of respondents disagree with the statement that it is “more difficult for remote workers to advance within the organization.” Although 31% are Neutral, a small majority (51%) either Strongly Agree or Moderately Agree with this statement.

chart 13: integration within the organization
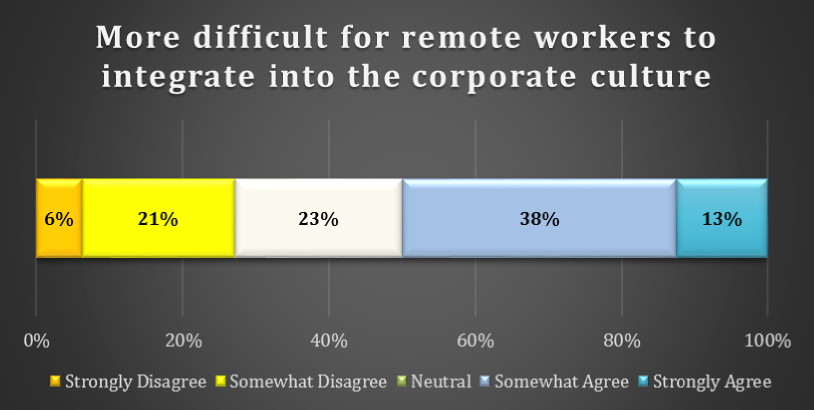
A small majority also believe that it is more difficult for remote workers to integrate into the corporate culture. Although only 13% of respondents Strongly Agree that it is more difficult to integrate, 38% Somewhat Agee. Only 6% of respondents Strongly Disagree with this statement. About one in five respondents (23%) are Neutral.
Management of Remote Workers
chart 14: difficulty managing remote workers
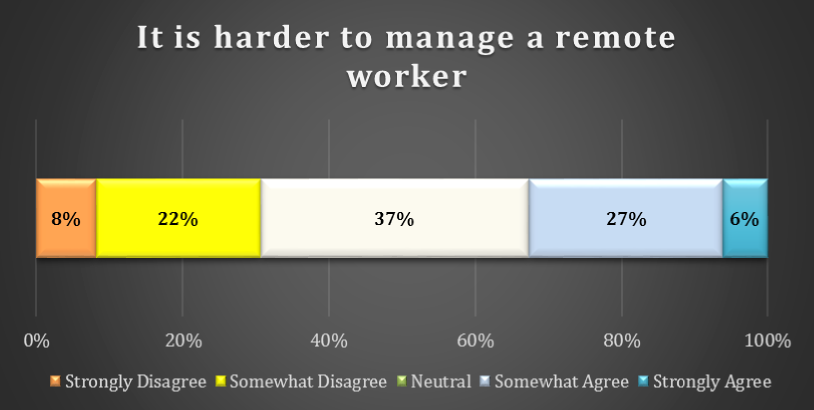
37% of respondents are Neutral as to whether it is more difficult to manage a remote worker. 27% indicate that they Somewhat Agree and a further 6% indicate that they Strongly Agree that remote workers are more difficult to manage. 8% of respondents Strongly Disagree and a further 22% Somewhat Disagree with this statement.
chart 15: preference FOR REMOTE workers
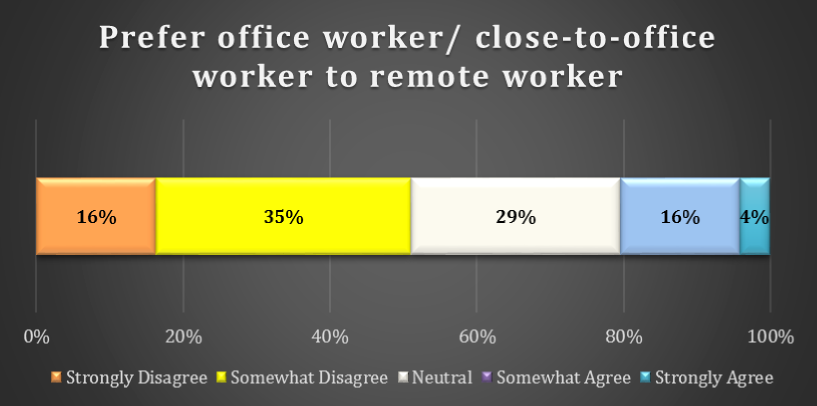
Only 20% of respondents prefer to hire office workers or close-to-office workers versus remote workers. 29% of respondents are neutral. Most respondents disagree with this suggestion: 16% Strongly Disagree and 35% Somewhat Disagree that they prefer office workers to remote workers.
chart 16: Management appreciation for remote workers
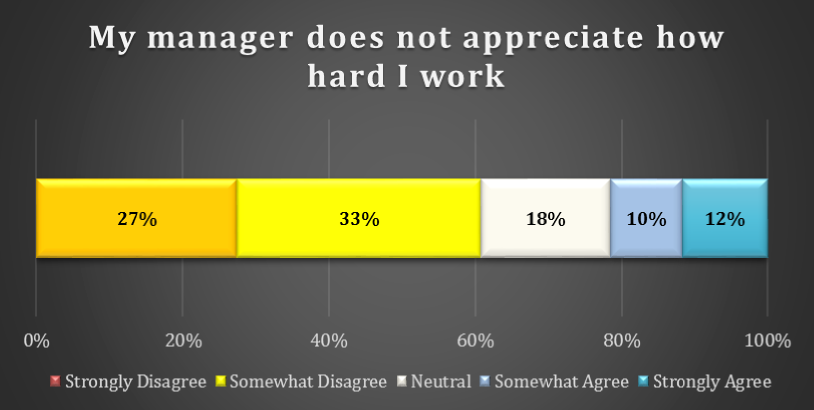
One in 5 respondents report that their manager does not appear how hard they work. Although 60% of respondents disagree with this statement, a minority do express this concern. A further 18% of respondents are Neutral.

Cost / Profitability Issues for Remote Workers
There is a general perspective that hiring remote workers is cheaper. This study identifies the drivers of costs savings and profitability.
chart 17: remote worker hours
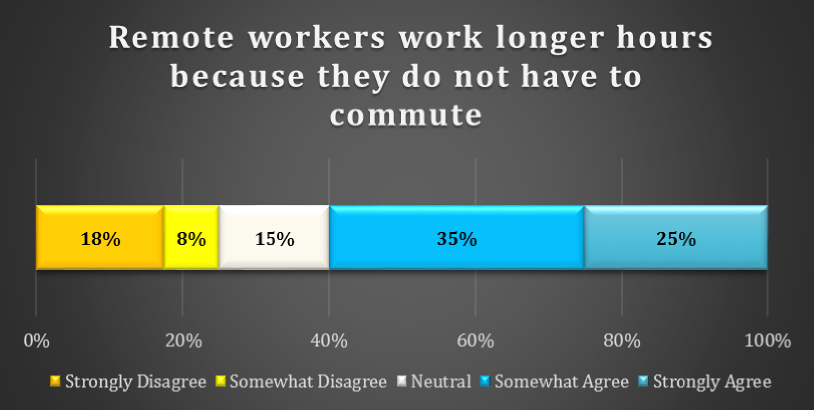
Employees can work a longer workday because they do not have to commute. Although number of hours is more of an indicator of productivity tha profitability, it is important to identify one of the key drivers of longer hours – lower commute time.
chart 18: overtime considerations for remote workers
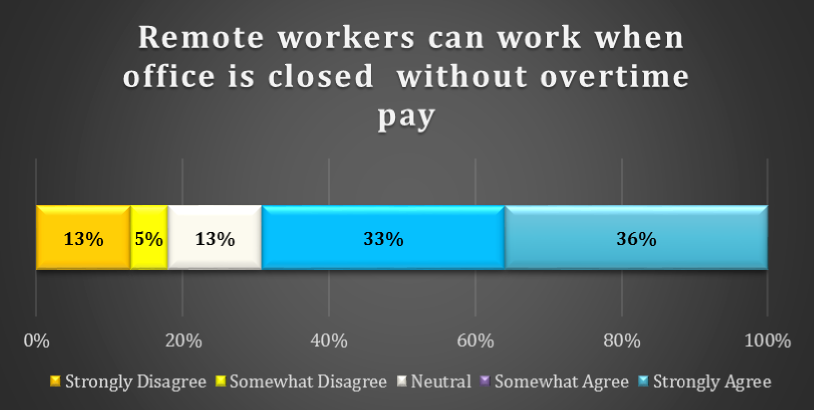
As indicated above, 69% of respondents Strongly Agree or Somewhat Agree with the statement that remote workers can work when the office is closed without receiving overtime pay.
chart 19: cost of remote workers
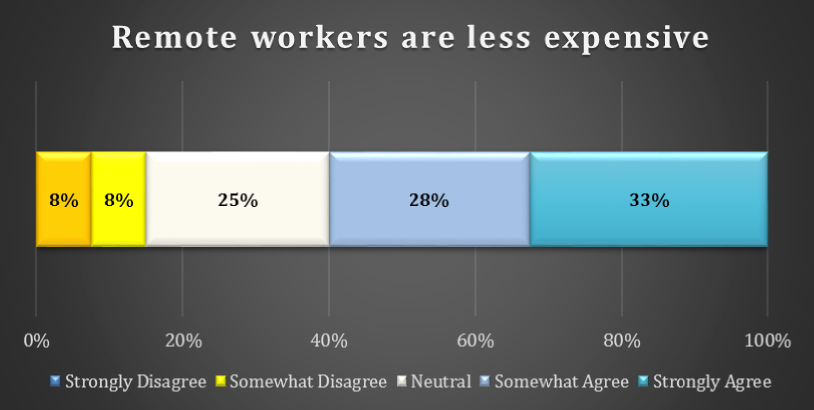
Are remote workers less expensive? Only 16% of respondents do not agree with this statement. 25% of respondents are neutral and 28% Somewhat Agree. A full 33% of respondents (one in every three) Strongly Agrees with the idea that remote workers are less expensive.

Technology Issues
Since the adoption of email, technology has been the single most powerful force supporting the trend towards remote working. We are respondents to identify the specific collaboration tools used by remote workers and to provide feedback on the impact of collaboration tools.
chart 20: technology tools for remote workers
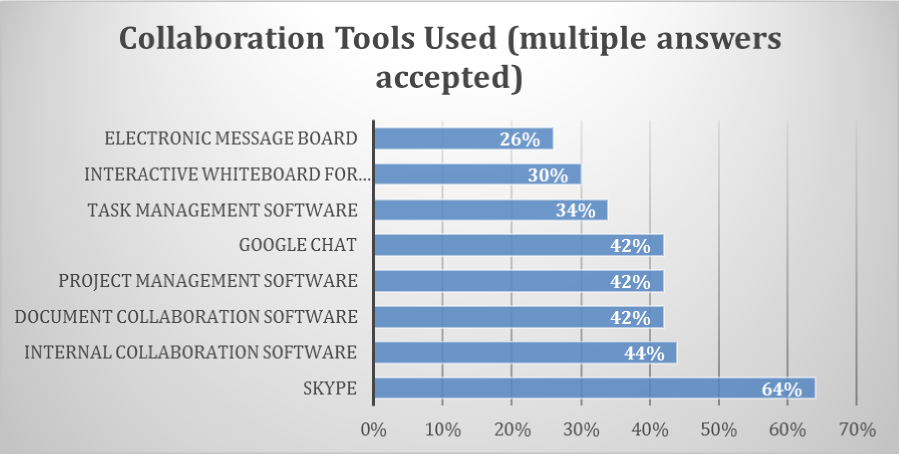
The most popular collaboration tool used by remote workers is Skype, which was used by 64% of all respondents. Internal collaboration tools were also very popular, with 44% of respondents indicating that they use them. As a general rule, Skype was most popular with startups and there was some fall-off in usage with larger organizations. Conversely, internal collaboration software was most common with Enterprise companies and less popular with startups small and organizations.
chart 21: role of technology supporting collaboration

Only 20% indicated that collaboration with remote teams is hard. 22% indicated that collaboration is easy, even though no collaboration tools are used. A further 58% stated that collaboration is easy and also attributable to the use of collaboration tools.

Conclusion
The Binfire Future of Remote Workers Survey shows that organizations benefit from remote workers. Respondents consider remote workers to be productive and hard working. In many cases, remote workers provide a unique and different perspective to problems. At the same time, remote workers often struggle to be part of the organizational corporate culture or to receive the recognition that they deserve.

Survey Methodology
Binfire conducted an online survey with over 150 qualified workers between May 30th and July 10th, 2016. The breakdown by segment is as follows: Startup (15%), Small Business with fewer than 100 employees (43%), Medium Business with 100 to 1,000 employees (19%), and Large business with 1,001+ employees (23%).
